Some of these date back to older versions but efforts are made to keep the most important - sometimes :)
LambdaStack backup design document
Affected version: 0.4.x
Goals
Provide backup functionality for LambdaStack - cluster created using lambdastack tool.
Backup will cover following areas:
-
1.1 etcd database
1.2 kubeadm config
1.3 certificates
1.4 persistent volumes
1.5 applications deployed on the cluster
-
2.1 Kafka topic data
2.2 Kafka index
2.3 Zookeeper settings and data
-
3.1 Elasticsearch data
3.2 Kibana settings
-
4.1 Prometheus data
4.2 Prometheus settings (properties, targets)
4.3 Alertmanager settings
4.4 Grafana settings (datasources, dashboards)
-
5.1 All databases from DB
Use cases
User/background service/job is able to backup whole cluster or backup selected parts and store files in desired location. There are few options possible to use for storing backup:
- S3
- Azure file storage
- local file
- NFS
Application/tool will create metadata file that will be definition of the backup - information that can be useful for restore tool. This metadata file will be stored within backup file.
Backup is packed to zip/gz/tar.gz file that has timestamp in the name. If name collision occurred name+'_1' will be used.
Example use
lsbackup -b /path/to/build/dir -t /target/location/for/backup
Where -b is path to build folder that contains Ansible inventory and -t contains target path to store backup.
Backup Component View
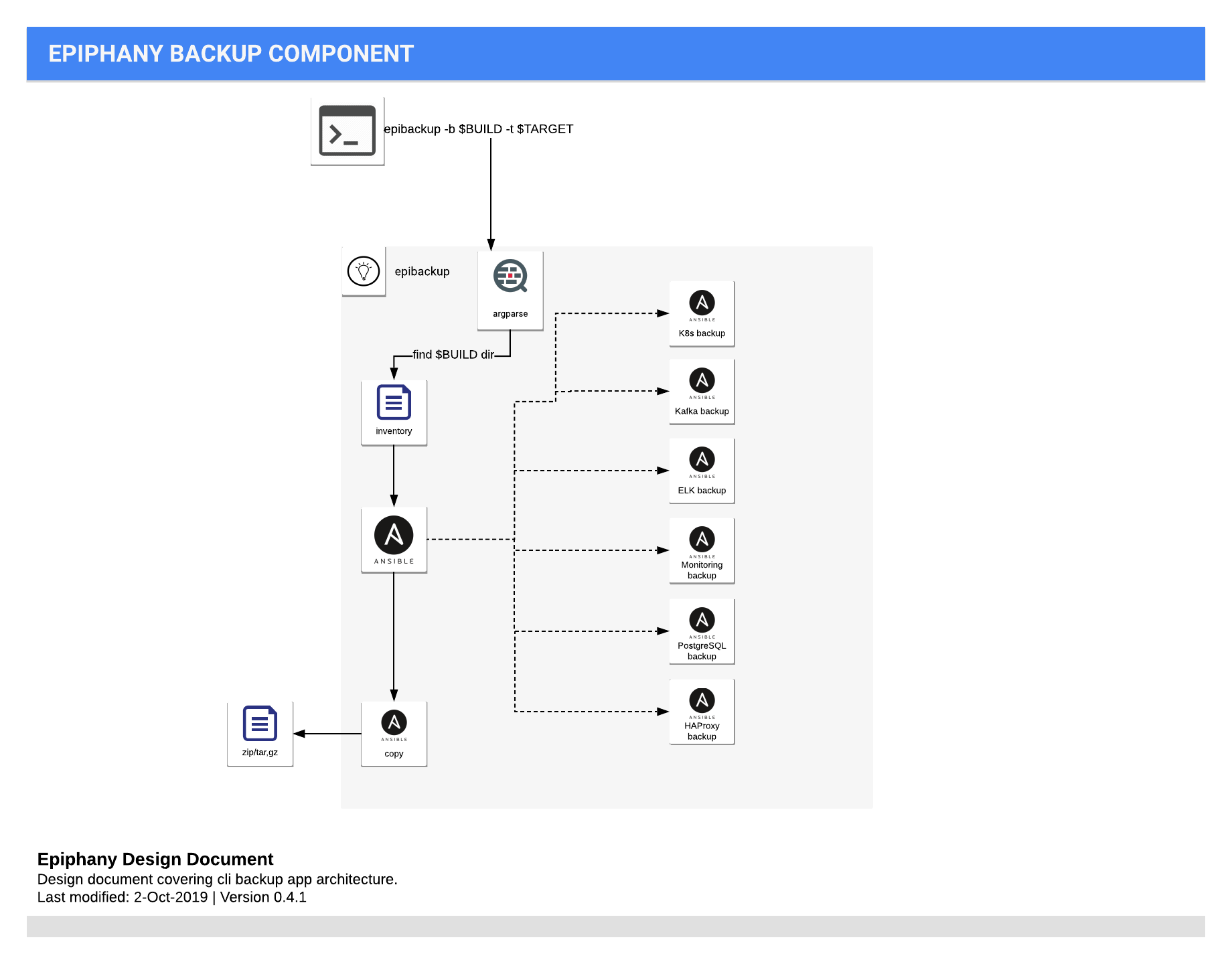
User/background service/job executes lsbackup (code name) application. Application takes parameters:
-b: build directory of existing cluster. Most important is ansible inventory existing in this directory - so it can be assumed that this should be folder of Ansible inventory file.-t: target location of zip/tar.gz file that will contain backup files and metadata file.
Tool when executed looks for the inventory file in -b location and executes backup playbooks. All playbooks are optional, in MVP version it can try to backup all components (it they exists in the inventory). After that, some components can be skipped (by providing additional flag, or parameter to cli).
Tool also produces metadata file that describes backup with time, backed up components and their versions.
1. Kubernetes cluster backup
There are few ways of doing backups of existing Kuberntes cluster. Going to take into further research two approaches.
First: Backup etcd database and kubeadm config of single master node. Instruction can be found here. Simple solution for that will backup etcd which contains all workload definitions and settings.
Second: Use 3rd party software to create a backup like Heptio Velero - Apache 2.0 license, Velero GitHub
2. Kafka backup
Possible options for backing up Kafka broker data and indexes:
-
Mirror using Kafka Mirror Maker. It requires second Kafka cluster running independently that will replicate all data (including current offset and consumer groups). It is used mostly for multi-cloud replication.
-
Kafka-connect – use Kafka connect to get all topic and offset data from Kafka an save to it filesystem (NFS, local, S3, ...) called Sink connector.
2.1 Confluent Kafka connector – that use Confluent Kafka Community License Agreement
2.2 Use another Open Source connector like kafka-connect-s3 (BSD) or kafka-backup (Apache 2.0) -
File system copy: take Kafka broker and ZooKeeper data stored in files and copy it to backup location. It requires Kafka Broker to be stopped. Solution described in Digital Ocean post.
3. Elastic stack backup
Use built-in features of Elasticsearch to create backup like:
PUT /_snapshot/my_unverified_backup?verify=false
{
"type": "fs",
"settings": {
"location": "my_unverified_backup_location"
}
}
More information can be found here.
OpenDistro uses similar way of doing backups - it should be compatible. OpenDistro backups link.
4. Monitoring backup
Prometheus from version 2.1 is able to create data snapshot by doing HTTP request:
curl -XPOST http://localhost:9090/api/v1/admin/tsdb/snapshot
Snapshot will be created in <data-dir>/snapshots/SNAPSHOT-NAME-RETURNED-IN-RESPONSE
Files like targets and Prometheus/AlertManager settings should be also copied to backup location.
5. PostgreSQL backup
Relational DB backup mechanisms are the most mature ones. Simplest solution is to use standard PostgreSQL backup funtions. Valid option is also to use pg_dump.
6. RabbitMQ settings and user data
RabbitMQ has standard way of creating backup.
7. HAProxy settings backup
Copy HAProxy configuration files to backup location.